Aerospace engineering is a highly technical field. Aerospace materials refer to those widely used in the aerospace sector, characterized primarily by being lightweight, high-strength, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant. These materials play a crucial role in aerospace applications. It is essential to conduct precise testing on aerospace materials to ensure their performance meets the stringent requirements for key components such as aircraft, aero-engines, and onboard equipment.

I. The Development History of Aerospace Materials:
In the early stages of aerospace engineering, metallic materials like aluminum alloys were predominantly used. These materials offered excellent mechanical properties and formability but suffered from high density, susceptibility to corrosion, and durability issues. With technological advancements and increasing aerospace demands, the field began adopting more advanced materials, such as polymer materials and composite materials. In the future, with further technological development and growing demands, aerospace materials are expected to have even broader prospects.
Polymer materials are materials with a high molecular structure, known for being lightweight, high-strength, and corrosion-resistant. In the aerospace industry, polymer materials are primarily used to manufacture components like aircraft fuselages and wings. For example, the fuselage of the Boeing 787 extensively uses carbon fiber-reinforced plastic. This material not only possesses high strength and stiffness but also has a density approximately 20%-30% lower than aluminum alloy, significantly reducing aircraft weight and fuel consumption.
Composite materials are composed of two or more different materials, offering excellent performance and multiple functionalities. In aerospace engineering, composites are widely used as structural materials for aircraft, rockets, and other vehicles. For instance, the US F-22 Raptor fighter jet extensively utilizes composite materials in its construction. These materials not only provide high strength and stiffness but can also withstand erosion from high temperatures and high-speed airflow.
Besides polymer and composite materials, several other materials are also widely used in aerospace engineering. For example, superconducting materials can be used in electromagnetic systems of aircraft, offering advantages like high efficiency, energy savings, and environmental friendliness. Nanomaterials can be used to manufacture high-strength, high-toughness components, exhibiting excellent mechanical and physical properties.
II. Precision Measurement Requirements for Aerospace Materials:
1. 3D Topography Inspection after Friction and Wear:
The aerospace sector has extremely high safety requirements for materials. Friction and wear are phenomena that occur during frictional contact, leading to surface wear and damage on materials.
Safety: Performing precise measurements of surface roughness and 3D topography helps assess the wear resistance of materials, ensuring that severe wear compromising safety does not occur during use, thereby guaranteeing the safety performance of the aircraft.
Life Prediction: The service life of aerospace vehicles is limited, and material friction and wear are significant factors leading to lifespan reduction. Through precise measurement of materials subjected to friction and wear, it is possible to predict the material's lifespan, allowing for timely maintenance and replacement measures to extend the service life of the aircraft.
Material Optimization: Optimizing aerospace materials is key to improving vehicle performance and efficiency. Through precise measurement of friction and wear, the wear performance of different materials can be evaluated, enabling the selection of the most suitable materials to enhance vehicle performance.
Below is a case study of the white light interferometer AM-7000 series inspecting the 3D topography of an alloy gasket after fretting wear:
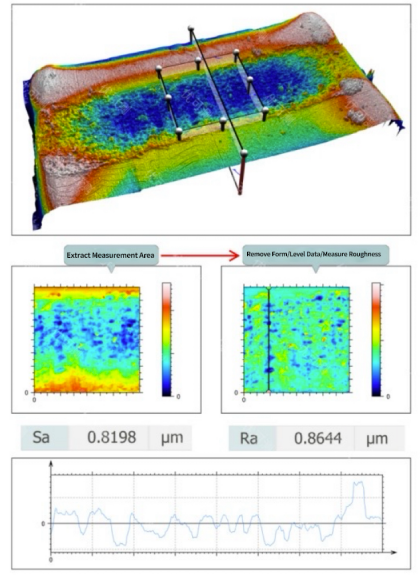
2. Surface Roughness/Smoothness and Curvature of Ultra-Smooth Components:
In the field of precision optics, components with an Ra value < 0.3nm are generally referred to as ultra-smooth components.
Reducing Aerodynamic Drag: In aerospace, aerodynamic drag is a critical issue. Higher surface smoothness results in lower aerodynamic drag. Combined with ultra-smooth components of appropriate curvature, this can enhance the speed and fuel efficiency of the aircraft. Therefore, it is necessary to inspect the curvature and surface smoothness of ultra-smooth component materials to ensure they meet design requirements.
Precision Machining Control: Ultra-smooth components typically require precision machining. Thus, measuring parameters such as curvature, surface roughness, and 3D topography of ultra-smooth components is essential to ensure the control accuracy of the precision machining meets requirements, guaranteeing processing quality and efficiency.
Surface Quality Assessment: Ultra-smooth components often require quality assessment to ensure that parameters like surface roughness and curvature comply with specifications. This necessitates precision measurement instruments with accuracy reaching the sub-nanometer level for inspection.
Below is a case study of the white light interferometer AM-7000 series inspecting the surface roughness of an ultra-smooth lens:
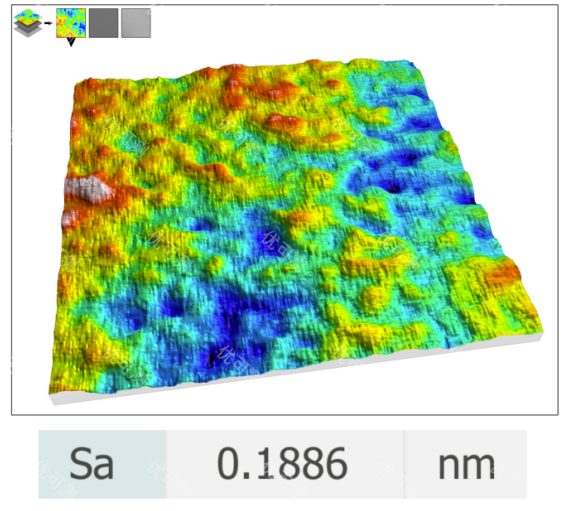
3. Dimensional Measurement and 3D Topography Inspection of Laser-Processed and Precision-Machined Components:
Dimensional Measurement: Aerospace materials have very high requirements for dimensional accuracy. Laser processing can achieve micron-level dimensional machining of materials. Precision measurement allows for accurate measurement of post-processed dimensions, assessing machining accuracy to ensure dimensions meet design requirements.
Quality Control: Precision measurement helps monitor the processing quality during laser machining, ensuring the results conform to design specifications and avoiding machining defects and quality issues. Laser processing can cause thermal effects and melting on the material surface, affecting surface quality. Precision measurement allows for the evaluation of material surfaces after laser processing, detecting issues like surface defects and melted zones, ensuring the material surface quality meets requirements.
Processing Optimization: The laser processing techniques for aerospace materials need continuous optimization to meet the requirements of different materials and processing needs. Precision measurement allows for the evaluation and optimization of processing techniques, improving processing quality and efficiency, and promoting the application and development of laser processing technology in the aerospace field.
Below is a case study of inspecting the step height after laser etching on a metal gasket and the topography of the machined central area:
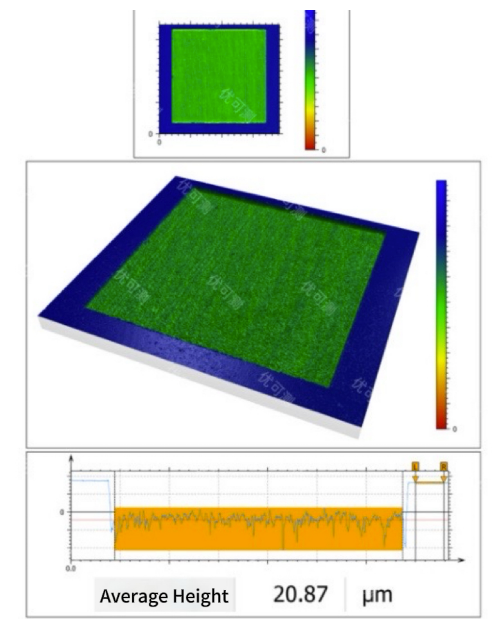
4. Coating and Film Thickness Inspection:
Protective Performance Evaluation: Coatings and films often serve protective functions in aerospace, such as anti-corrosion, high-temperature resistance, and wear resistance. The protective performance of a coating is closely related to its thickness. Therefore, precise measurement of coating thickness helps assess whether the coating's protective performance meets requirements.
Material Performance Optimization: The performance of coatings and films is often related to their thickness; for instance, the thermal insulation properties of certain coatings or films strengthen with increasing thickness. By precisely measuring coating thickness, the impact of different thicknesses on performance can be evaluated, allowing for optimization of coating and film thickness to achieve optimal performance.
Quality Control: Coating and film thickness is an important quality indicator, as deviations in thickness can lead to performance variations. Precise measurement of coating thickness helps monitor quality during the coating preparation process, ensuring the thickness conforms to design requirements and avoiding coating quality issues.
Precision Coating/Film Preparation: Precise measurement of coating and film thickness enables control over thickness uniformity and consistency, improving the quality and performance of coatings and films.
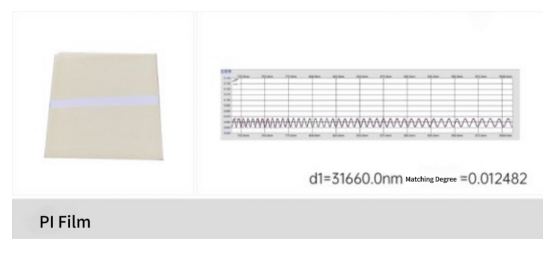
Polyimide (PI) films typically feature characteristics such as radiation resistance, high-temperature resistance, low-temperature resistance, high transparency, low moisture absorption, low dielectric constant, and low dielectric loss, playing a significant role in the aerospace field. Below is a case study of the film thickness measurement instrument AF-3000 series inspecting the thickness of a PI film:
Atometrics White Light Interferometer AM-7000 Series offers sub-nanometer level accuracy;
Maximum RMS repeatability up to 0.002nm;
Equipped with piezoelectric ceramic components, maximum scanning speed of 400μm/s;
With 3200Hz and the industry-first SST+GAT algorithm,
It can instantly complete the collection of up to 5 million point clouds;
Covers commonly used international standard measurement tools in the market,
Efficiently and easily analyzes 3D data, calmly meeting application needs across various industries.
Atometrics Film Thickness Measurement Instrument AF-3000 Series offers accuracy up to 0.1nm;
Rich application scenarios, suitable for offline, online, Mapping, and other scenarios;
Can measure up to 10 film layers simultaneously, also supports customization.